|
|
前言
Scriptable Build Pipeline 是什么?能来带什么好处?
- 自定义 Unity 如何构建应用内容
- 将原先处于C++的引擎代码移到了C#
- 加速了AssetBundle的构建时间
- 改善增量构建处理
- 对开发者来说具备更多的灵活性
Unity版本要求
术语
磁盘上的源文件,通常位于项目的 “Assets” 文件夹中。
此文件在内部导入到您的资产的可用于游戏的表示形式,其中可以包含多个 Object(SubAsset)。
单个Unity可序列化单元。也称为SubAsset。导入的Asset由一个或多个对象组成。
从中构造Asset的唯一 一组Object。
一组 需要被 Asset 使用,但不在该 Asset 中 的Object。 快速入门 & BuildIn切换
BuildAssetBundles
BuildIn Pipeline
using System.IO;
using UnityEditor;
public static class BuildAssetBundlesExample
{
public static bool BuildAssetBundles(string outputPath, bool forceRebuild, bool useChunkBasedCompression, BuildTarget buildTarget)
{
var options = BuildAssetBundleOptions.None;
if (useChunkBasedCompression)
options |= BuildAssetBundleOptions.ChunkBasedCompression;
if (forceRebuild)
options |= BuildAssetBundleOptions.ForceRebuildAssetBundle;
Directory.CreateDirectory(outputPath);
var manifest = BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles(outputPath, options, buildTarget);
return manifest != null;
}
}
SBP
- CompatibilityBuildPipeline 是SBP 目前官方使用SBP流程适配 BuildIn流程的 适配实现。
SBP不支持以前支持的 所有 功能。 using System.IO;
using UnityEditor;
// Added new using
using UnityEditor.Build.Pipeline;
public static class BuildAssetBundlesExample
{
public static bool BuildAssetBundles(string outputPath, bool forceRebuild, bool useChunkBasedCompression, BuildTarget buildTarget)
{
var options = BuildAssetBundleOptions.None;
if (useChunkBasedCompression)
options |= BuildAssetBundleOptions.ChunkBasedCompression;
if (forceRebuild)
options |= BuildAssetBundleOptions.ForceRebuildAssetBundle;
Directory.CreateDirectory(outputPath);
// Replaced BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles with CompatibilityBuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles here
var manifest = CompatibilityBuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles(outputPath, options, buildTarget);
return manifest != null;
}
}
注意事项
CompatibilityBuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles vs BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundle 的特性与行为的对比
| 特性 | 是否支持 | 说明 | | AssetBundles | 支持 | 与原流程基本一致 | | 增量构建 | 支持 | SBP对于增量构建的逻辑封装为 `BuildCache` 类实现。 | | 关于资源加载的路径参数 | 行为变更 | 原有构建的 AssetBundle 支持两种入参形式:全路径(`Assets/ExampleFolder/Asset.prefab`) 、文件名(`Asset`、`Asset.prefab`)
SBP构建的 AssetBundle 仅支持全路径(``Assets/ExampleFolder/Asset.prefab`)的入参。如果需要重载加载时的入参,可使用`IBundleBuildContent.Addresses` 或 [AssetBundleBuild.addressableNames](https://docs.unity3d.com/ScriptReference/AssetBundleBuild-addressableNames.html) 推荐使用 SBP中的 `IBundleBuildContent` 有利于构建流程的统一和开发便利性。 | | AssetBundle Manifest | 行为变更 | SBP 提供了 ``CompatibilityAssetBundleManifest`` 来适配 原来的 Manifest,并且新增了获取 Bundle CRC的接口 | | AssetBundle Variants | 不支持 | 目前SBP没有提供变体的支持;个人也不推荐使用。 |
BuildAssetBundleOptions
| Value | 是否支持 | 说明 | | UncompressedAssetBundle | 支持 | 等价于 BuildCompression.DefaultUncompressed | | ChunkBasedCompression | 支持 | 持等价于 `BuildCompression.DefaultLZ4`.
需要注意的是: 在编辑器下 采用 LZ4HC,若是运行时重新压缩的话将采用LZ4 | | DisableWriteTypeTree | 支持 | 等价于 `ContentBuildFlags.DisableWriteTypeTree` | | DeterministicAssetBundle | 支持 | 默认开启,并且不能关闭。SBP的构建是资源确定性,这对于需要支持资源更新的游戏是好处 | | ForceRebuildAssetBundle | 支持 | 等价于 `IBuildParameters.UseCache = false;` | | AppendHashToAssetBundleName | 支持 | 等价于 `IBundleBuildParameters.AppendHash = true;` | | DisableLoadAssetByFileName | 总是开启 | 默认开启,并且不能关闭。SBP遵循的原则是 构建时的入参即是运行时的入参;
加载入参要求:**大小写**、**标点符号** 与构建时的参数一致 | | DisableLoadAssetByFileNameWithExtension | 总是开启 | 类比于 DisableLoadAssetByFileName 的逻辑 | | IgnoreTypeTreeChanges | 不支持 | SBP的增量构建系统 使用 TypeTree作为数据是否变更的依据,来防止Asset数据没有修改,而序列化结构变更导致的重新构建 | | StrictMode | 不支持 | SBP严格要求正确构建AssetBundles并知道何时构建失败 | | DryRunBuild | 不支持 | SBP的工作原理根本不同,进行完整构建以确定是否已更改的速度更快 |
AssetBundle SBP 构建流程
1.Setup - 平台环境初始化
- SwitchToBuildPlatform
- RebuildSpriteAtlasCache
2.Player Scripts - 工程源代码编译
- BuildPlayerScripts
- PostScriptsCallback
3.Dependency
- CalculateSceneDependencyData
- CalculateCustomDependencyData (UNITY_2019_3_OR_NEWER)
- CalculateAssetDependencyData
- StripUnusedSpriteSources
- PostDependencyCallback
4.Packing
- GenerateBundlePacking
- GenerateBundleCommands
- GenerateSubAssetPathMaps
- GenerateBundleMaps
- PostPackingCallback
5.Writing
- WriteSerializedFiles
- ArchiveAndCompressBundles
- AppendBundleHash
- GenerateLinkXml
- PostWritingCallback
6.Generate manifest files
Setup
SwitchToBuildPlatform
- 切换 当前平台 为构建AssetBundle的 目标平台 对应的 BuildTargetGroup 、 BuildTarget
- 执行回调 IPreprocessShaders 、IProcessScene、IProcessSceneWithReport
关键逻辑:
EditorUserBuildSettings.SwitchActiveBuildTarget(m_Parameters.Group, m_Parameters.Target);
RebuildSpriteAtlasCache
- 针对目标平台 重新构建 工程内所有的 SpriteAtlas
关键逻辑:
SpriteAtlasUtility.PackAllAtlases(m_Parameters.Target);
Player Scripts
BuildPlayerScripts
- 编译 目标平台 源代码 生成 ScriptInfo(TypeDB - 记录了脚本类型 、 属性数据)
TypeDB 为后续的序列化 提供 正确的字段名称; 关键逻辑:
PlayerBuildInterface.CompilePlayerScripts(m_Parameters.GetScriptCompilationSettings(), m_Parameters.ScriptOutputFolder);
PostScriptsCallback
上层开发者,注册监听 BuildCallbacks.PostScriptsCallbacks 关键逻辑:
IScriptsCallback.PostScripts(IBuildParameters parameters, IBuildResults results);
Dependency
CalculateSceneDependencyData - 计算所有场景的依赖信息
- 判断是否使用 Cache 机制
- 计算场景相关依赖项
关键逻辑:
#if UNITY_2019_3_OR_NEWER
ContentBuildInterface.CalculatePlayerDependenciesForScene(scenePath, settings, usageTags, m_DependencyData.DependencyUsageCache);
#else
ContentBuildInterface.PrepareScene(scenePath, settings, usageTags, m_DependencyData.DependencyUsageCache, outputFolder);
#endif
Cache 仅记录 预制相关的依赖 CalculateCustomDependencyData (UNITY_2019_3_OR_NEWER)
计算未被 AssetDatabase 追踪的 自定义 Assets 依赖的 Object关系
由 IBundleBuildContent.CustomAssets 自定义 AssetBundle包含的内容
关键逻辑:
foreach (CustomContent info in IBundleBuildContent.CustomAssets)
{
info.Processor(info.Asset, this);
}
CalculateAssetDependencyData - 计算所有 Asset的依赖数据
- 基础入参
- 源代码的 TypeDB
- GraphicsSettings
- 场景的LightSetting
- 获取 Asset 的 所包含的 Objects
即为 该Asset引用的 Object;为 该 Asset YAML 序列化中 !u![ClassID] 段所表示的 Object。
- 通过 TypeDB 获取 Objects 所引用的 Objects
- 如果是 Sprite 类型资源,则进行 Sprite Atlas 的打包设置
- 计算 SubAssets
关键逻辑:
var includedObjects = ContentBuildInterface.GetPlayerObjectIdentifiersInAsset(asset, input.Target);
var referencedObjects = ContentBuildInterface.GetPlayerDependenciesForObjects(includedObjects, input.Target, input.TypeDB);
ObjectIdentifier[] representations = ContentBuildInterface.GetPlayerAssetRepresentations(asset, target);
// Main Asset always returns at index 0, we only want representations, so check for greater than 1 length
if (representations.IsNullOrEmpty() || representations.Length < 2)
return;
extendedData = new ExtendedAssetData();
extendedData.Representations.AddRange(representations.Skip(1));
StripUnusedSpriteSources - 删除 Assets引用中被Packer的Sprite
- 筛选出 已经被 SpritePacker 打包的Sprite,所归属的 SourceTexture
- 删除 Assets 中引用的 Sprite信息
关键逻辑:
var unusedSources = new HashSet<ObjectIdentifier>();
var textures = m_SpriteData.ImporterData.Values.Where(x => x.PackedSprite).Select(x => x.SourceTexture);
unusedSources.UnionWith(textures);
// Count refs from assets
var assetRefs = m_DependencyData.AssetInfo.SelectMany(x => x.Value.referencedObjects);
foreach (ObjectIdentifier reference in assetRefs)
unusedSources.Remove(reference);
// Count refs from scenes
var sceneRefs = m_DependencyData.SceneInfo.SelectMany(x => x.Value.referencedObjects);
foreach (ObjectIdentifier reference in sceneRefs)
unusedSources.Remove(reference);
// SetOutputInformation
foreach (var source in unusedSources)
{
var assetInfo = m_DependencyData.AssetInfo[source.guid];
assetInfo.includedObjects.RemoveAt(0);
ExtendedAssetData extendedData;
if (m_ExtendedAssetData != null && m_ExtendedAssetData.ExtendedData.TryGetValue(source.guid, out extendedData))
{
extendedData.Representations.Remove(source);
if (extendedData.Representations.Count == 1)
m_ExtendedAssetData.ExtendedData.Remove(source.guid);
}
}
PostDependencyCallback
上层开发者,注册监听 BuildCallbacks.PostDependencyCallback 关键逻辑:
IDependencyCallback.PostDependency(IBuildParameters parameters, IDependencyData dependencyData);
Packing - 资源构建
GenerateBundlePacking - 组装AssetBundle以及计算依赖加载列表
Normal AssetBundle
Streamed Scene AssetBundle
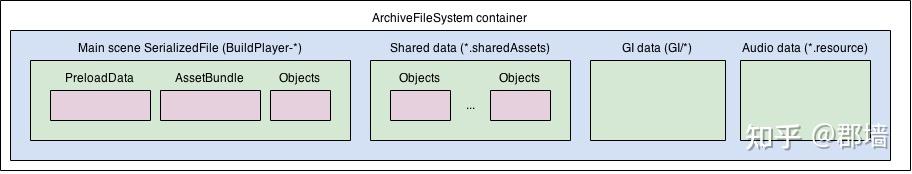
ArchiveFileSystem
- 校验 Object 是否是 Assets 类型 或 自定义Assets类型 | Scene 类型,创建对应类型的 “容器结构”
可通过 ValidationMethods.ValidAssetFake 接管 校验逻辑 - 剔除 Unity默认的内置资源引用
- 处理依赖关系中的重复递归依赖 & 打破环形依赖;(若是 Scene Bundle,则剔除 sharedAssets 的重复引用) 关键逻辑:
foreach (var bundle in m_BuildContent.BundleLayout)
{
if (ValidAssetBundle(bundle.Value, customAssets))
PackAssetBundle(bundle.Key, bundle.Value, assetToReferences);
else if (ValidationMethods.ValidSceneBundle(bundle.Value))
PackSceneBundle(bundle.Key, bundle.Value, assetToReferences);
}
// Remove Default Resources and Includes for Assets assigned to Bundles
foreach (ObjectIdentifier reference in references)
{
if (reference.filePath.Equals(CommonStrings.UnityDefaultResourcePath, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
continue;
if (dependencyData.AssetInfo.TryGetValue(reference.guid, out AssetLoadInfo referenceInfo))
{
referencedAssets.Add(referenceInfo);
continue;
}
referencesPruned.Add(reference);
}
var referencedAssetsGuids = new List<GUID>(referencedAssets.Count);
// Remove References also included by non-circular Referenced Assets
// Remove References also included by circular Referenced Assets if Asset&#39;s GUID is higher than Referenced Asset&#39;s GUID
foreach (AssetLoadInfo referencedAsset in referencedAssets)
{
var refObjectIdLookup = new HashSet<ObjectIdentifier>(referencedAsset.referencedObjects);
bool circularRef = refObjectIdLookup.Select(x => x.guid).Contains(asset);
if (!circularRef || (circularRef && asset > referencedAsset.asset || asset == referencedAsset.asset))
references.RemoveAll(refObjectIdLookup.Contains);
referencedAssetsGuids.Add(referencedAsset.asset);
}
// Special path for scenes, they can use data from previous sharedAssets in the same bundle
if (!previousSceneObjects.IsNullOrEmpty())
references.RemoveAll(previousSceneObjects.Contains);
GenerateBundleCommands - 为需要序列化的AssetBundle创建WriteOperation行为
- 初始化 AssetBundle MainAsset
- 创建对应的 BundleCommand (CreateAssetBundleCommand、CreateSceneBundleCommand + CreateSceneDataCommand)
AssetBundleCommand :
1.建立加载 Asset的入参 与 Object的映射关系
2.记录 AssetsBundle 中包含的Assets相关信息(依赖的Object hash、序列化组织形式等)并排序,以此确保每次序列化数据的稳定性
SceneBundleCommand :
1.建立加载 Scene 所包含需要序列化的Object与 加载的入参的映射关系
2.记录 SceneBundle 依赖的Object 至 preloadObjects
SceneDataCommand :
1.建立加载Scene 所需要附加的Assets 的映射关系
2.记录 SceneBundle 依赖的Object 至 preloadObjects 关键逻辑:
Dictionary<GUID, string> assetToMainFile = new Dictionary<GUID, string>();
foreach (var pair in m_WriteData.AssetToFiles)
assetToMainFile.Add(pair.Key, pair.Value[0]);
foreach (var bundlePair in m_BuildContent.BundleLayout)
{
if (ValidAssetBundle(bundlePair.Value, customAssets))
{
// Use generated internalName here as we could have an empty asset bundle used for raw object storage (See CreateStandardShadersBundle)
var internalName = string.Format(CommonStrings.AssetBundleNameFormat, m_PackingMethod.GenerateInternalFileName(bundlePair.Key));
CreateAssetBundleCommand(bundlePair.Key, internalName, bundlePair.Value);
}
else if (ValidationMethods.ValidSceneBundle(bundlePair.Value))
{
var firstScene = bundlePair.Value[0];
CreateSceneBundleCommand(bundlePair.Key, assetToMainFile[firstScene], firstScene, bundlePair.Value, assetToMainFile);
for (int i = 1; i < bundlePair.Value.Count; ++i)
{
var additionalScene = bundlePair.Value;
CreateSceneDataCommand(assetToMainFile[additionalScene], additionalScene);
}
}
}
GenerateSubAssetPathMaps
- 向 AssetBundle里插入 扩展资源 (“依赖资源”)
关键逻辑:
Dictionary<string, IWriteOperation> fileToOperation = m_WriteData.WriteOperations.ToDictionary(x => x.Command.internalName, x => x);
foreach (var pair in m_ExtendedAssetData.ExtendedData)
{
GUID asset = pair.Key;
string mainFile = m_WriteData.AssetToFiles[asset][0];
var abOp = fileToOperation[mainFile] as AssetBundleWriteOperation;
int assetInfoIndex = abOp.Info.bundleAssets.FindIndex(x => x.asset == asset);
AssetLoadInfo assetInfo = abOp.Info.bundleAssets[assetInfoIndex];
int offset = 1;
foreach (var subAsset in pair.Value.Representations)
{
var secondaryAssetInfo = CreateSubAssetLoadInfo(assetInfo, subAsset);
abOp.Info.bundleAssets.Insert(assetInfoIndex + offset, secondaryAssetInfo);
offset++;
}
}
GenerateBundleMaps - 前向依赖 & 反向依赖
1.计算 前向依赖 & 反向依赖
前向依赖 : 记录 AssetBundle中Object依赖其他的AssetBundle的Object 信息
反向依赖 : 记录包中资源数据被其他源AssetBundle依赖的信息 2.使用依赖关系简化引用映射以及Object构建方式
关键逻辑:
// BuildReferenceMap details what objects exist in other bundles that objects in a source bundle depend upon (forward dependencies)
// BuildUsageTagSet details the conditional data needed to be written by objects in a source bundle that is in used by objects in other bundles (reverse dependencies)
using (m_Log.ScopedStep(LogLevel.Info, $&#34;Temporary Map Creations&#34;))
{
fileToCommand = m_WriteData.WriteOperations.ToDictionary(x => x.Command.internalName, x => x.Command);
forwardObjectDependencies = new Dictionary<string, HashSet<ObjectIdentifier>>();
forwardFileDependencies = new Dictionary<string, HashSet<string>>();
reverseAssetDependencies = new Dictionary<string, HashSet<GUID>>();
foreach (var pair in m_WriteData.AssetToFiles)
{
GUID asset = pair.Key;
List<string> files = pair.Value;
// The includes for an asset live in the first file, references could live in any file
forwardObjectDependencies.GetOrAdd(files[0], out HashSet<ObjectIdentifier> objectDependencies);
forwardFileDependencies.GetOrAdd(files[0], out HashSet<string> fileDependencies);
// Grab the list of object references for the asset or scene and add them to the forward dependencies hash set for this file (write command)
if (m_DependencyData.AssetInfo.TryGetValue(asset, out AssetLoadInfo assetInfo))
objectDependencies.UnionWith(assetInfo.referencedObjects);
if (m_DependencyData.SceneInfo.TryGetValue(asset, out SceneDependencyInfo sceneInfo))
objectDependencies.UnionWith(sceneInfo.referencedObjects);
// Grab the list of file references for the asset or scene and add them to the forward dependencies hash set for this file (write command)
// While doing so, also add the asset to the reverse dependencies hash set for all the other files it depends upon.
// We already ensure BuildReferenceMap & BuildUsageTagSet contain the objects in this write command in GenerateBundleCommands. So skip over the first file (self)
for (int i = 1; i < files.Count; i++)
{
fileDependencies.Add(files);
reverseAssetDependencies.GetOrAdd(files, out HashSet<GUID> reverseDependencies);
reverseDependencies.Add(asset);
}
}
}
// Using the previously generated forward dependency maps, update the BuildReferenceMap per WriteCommand to contain just the references that we care about
using (m_Log.ScopedStep(LogLevel.Info, $&#34;Populate BuildReferenceMaps&#34;))
{
foreach (var operation in m_WriteData.WriteOperations)
{
var internalName = operation.Command.internalName;
BuildReferenceMap referenceMap = m_WriteData.FileToReferenceMap[internalName];
if (!forwardObjectDependencies.TryGetValue(internalName, out var objectDependencies))
continue; // this bundle has no external dependencies
if (!forwardFileDependencies.TryGetValue(internalName, out var fileDependencies))
continue; // this bundle has no external dependencies
foreach (string file in fileDependencies)
{
WriteCommand dependentCommand = fileToCommand[file];
foreach (var serializedObject in dependentCommand.serializeObjects)
{
// Only add objects we are referencing. This ensures that new/removed objects to files we depend upon will not cause a rebuild
// of this file, unless are referencing the new/removed objects.
if (!objectDependencies.Contains(serializedObject.serializationObject))
continue;
referenceMap.AddMapping(file, serializedObject.serializationIndex, serializedObject.serializationObject);
}
}
}
}
// Using the previously generate reverse dependency map, create the BuildUsageTagSet per WriteCommand to contain just the data that we care about
using (m_Log.ScopedStep(LogLevel.Info, $&#34;Populate BuildUsageTagSet&#34;))
{
foreach (var operation in m_WriteData.WriteOperations)
{
var internalName = operation.Command.internalName;
BuildUsageTagSet fileUsage = m_WriteData.FileToUsageSet[internalName];
if (reverseAssetDependencies.TryGetValue(internalName, out var assetDependencies))
{
foreach (GUID asset in assetDependencies)
{
if (m_DependencyData.AssetUsage.TryGetValue(asset, out var assetUsage))
fileUsage.UnionWith(assetUsage);
if (m_DependencyData.SceneUsage.TryGetValue(asset, out var sceneUsage))
fileUsage.UnionWith(sceneUsage);
}
}
if (ReflectionExtensions.SupportsFilterToSubset)
fileUsage.FilterToSubset(m_WriteData.FileToObjects[internalName].ToArray());
}
}
PostPackingCallback
上层开发者,注册监听 BuildCallbacks.PostPackingCallback 关键逻辑:
IPackingCallback.PostPacking(IBuildParameters parameters, IDependencyData dependencyData, IWriteData writeData);
Writing
WriteSerializedFiles - 序列化前奏 - MetaData
1.获取 GraphicsSettings、TypeDB 、目标平台 、 ContentBuildFlags
//
// 摘要:
// Build options for content.
[Flags]
public enum ContentBuildFlags
{
//
// 摘要:
// Build content with no additional options.
None = 0,
//
// 摘要:
// Do not include type information within the built content.
DisableWriteTypeTree = 1,
//
// 摘要:
// Build Flag to indicate the Unity Version should not be written to the serialized
// file.
StripUnityVersion = 2,
//
// 摘要:
// Build a development version of the content files.
DevelopmentBuild = 4
}
2. 查询缓存系统,构建缓存对象与需要重建的对象
3. 计算需要重建对象的 SerializedFileMetaData
Hash算法
- SpookyHash
- MD5
- MD4
- 可扩展 HasingMethods.GetHashAlgorithm 自定义 Hash算法
[Serializable]
public class SerializedFileMetaData
{
/// <summary>
/// A hash of all the serialized files
/// </summary>
public Hash128 RawFileHash;
/// <summary>
/// Hash of file contents. Some resource files may choose to exclude sections of their content from this hash. For example,
/// serialized files exclude the header of their content which allows this hash not to change with new Unity versions.
/// </summary>
public Hash128 ContentHash;
}
关键逻辑:
private SerializedFileMetaData CalculateFileMetadata(ref WriteResult result)
{
List<object> contentHashObjects = new List<object>();
List<object> fullHashObjects = new List<object>();
foreach (ResourceFile file in result.resourceFiles)
{
RawHash fileHash = HashingMethods.CalculateFile(file.fileName);
RawHash contentHash = fileHash;
fullHashObjects.Add(fileHash);
if (file.serializedFile && result.serializedObjects.Count > 0)
{
using (var stream = new FileStream(file.fileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read))
{
stream.Position = (long)result.serializedObjects[0].header.offset;
contentHash = HashingMethods.CalculateStream(stream);
}
}
contentHashObjects.Add(contentHash);
}
SerializedFileMetaData data = new SerializedFileMetaData();
data.RawFileHash = HashingMethods.Calculate(fullHashObjects).ToHash128();
data.ContentHash = HashingMethods.Calculate(contentHashObjects).ToHash128();
return data;
}
ArchiveAndCompressBundles - 规整&数据压缩
- 构造 Task 对象用于抽象线程化支持
- 合并资源文件并根据压缩选项进行压缩 (该行为基于是否支持多线程运行坏境有所不同)
- 比较缓存文件与输出目录文件时间戳,若不同则拷贝缓存文件覆盖至输出文件路径
关键逻辑:
item.ResultDetails = new BundleDetails();
string writePath = string.Format(&#34;{0}/{1}&#34;, tempOutputFolder, item.BundleName);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(item.CachedArtifactPath))
writePath = item.CachedArtifactPath;
Directory.CreateDirectory(Path.GetDirectoryName(writePath));
item.ResultDetails.FileName = item.OutputFilePath;
item.ResultDetails.Crc = ContentBuildInterface.ArchiveAndCompress(item.ResourceFiles.ToArray(), writePath, item.Compression);
CopyFileWithTimestampIfDifferent(writePath, item.ResultDetails.FileName, log);
AppendBundleHash - 追加Hash信息
- 仅在 AppendHashToAssetBundleName 开启才执行
关键逻辑:
string[] bundles = m_Results.BundleInfos.Keys.ToArray();
foreach (string bundle in bundles)
{
var details = m_Results.BundleInfos[bundle];
var oldFileName = details.FileName;
var newFileName = string.Format(&#34;{0}_{1}&#34;, details.FileName, details.Hash.ToString());
details.FileName = newFileName;
m_Results.BundleInfos[bundle] = details;
File.Delete(newFileName);
File.Move(oldFileName, newFileName);
}
GenerateLinkXml - 生成AssetBundle使用的Link文件,便于代码裁剪
建议开启 IBuildParameters.WriteLinkXML
- 仅在 IBuildParameters.WriteLinkXML 选项开启执行
关键逻辑:
var linker = LinkXmlGenerator.CreateDefault();
foreach (var writeResult in m_Results.WriteResults)
{
linker.AddTypes(writeResult.Value.includedTypes);
#if UNITY_2021_1_OR_NEWER
linker.AddSerializedClass(writeResult.Value.includedSerializeReferenceFQN);
#else
if (writeResult.Value.GetType().GetProperty(&#34;includedSerializeReferenceFQN&#34;) != null)
{
linker.AddSerializedClass(writeResult.Value.GetType().GetProperty(&#34;includedSerializeReferenceFQN&#34;).GetValue(writeResult.Value) as System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<string>);
}
#endif
}
var linkPath = m_Parameters.GetOutputFilePathForIdentifier(k_LinkXml);
linker.Save(linkPath);
PostWritingCallback
上层开发者,注册监听 BuildCallbacks.PostWritingCallback 关键逻辑:
IWritingCallback.PostWriting(IBuildParameters parameters, IDependencyData dependencyData, IWriteData writeData, IBuildResults results);
结语:
知乎的Markdown真难用! |
本帖子中包含更多资源
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
|